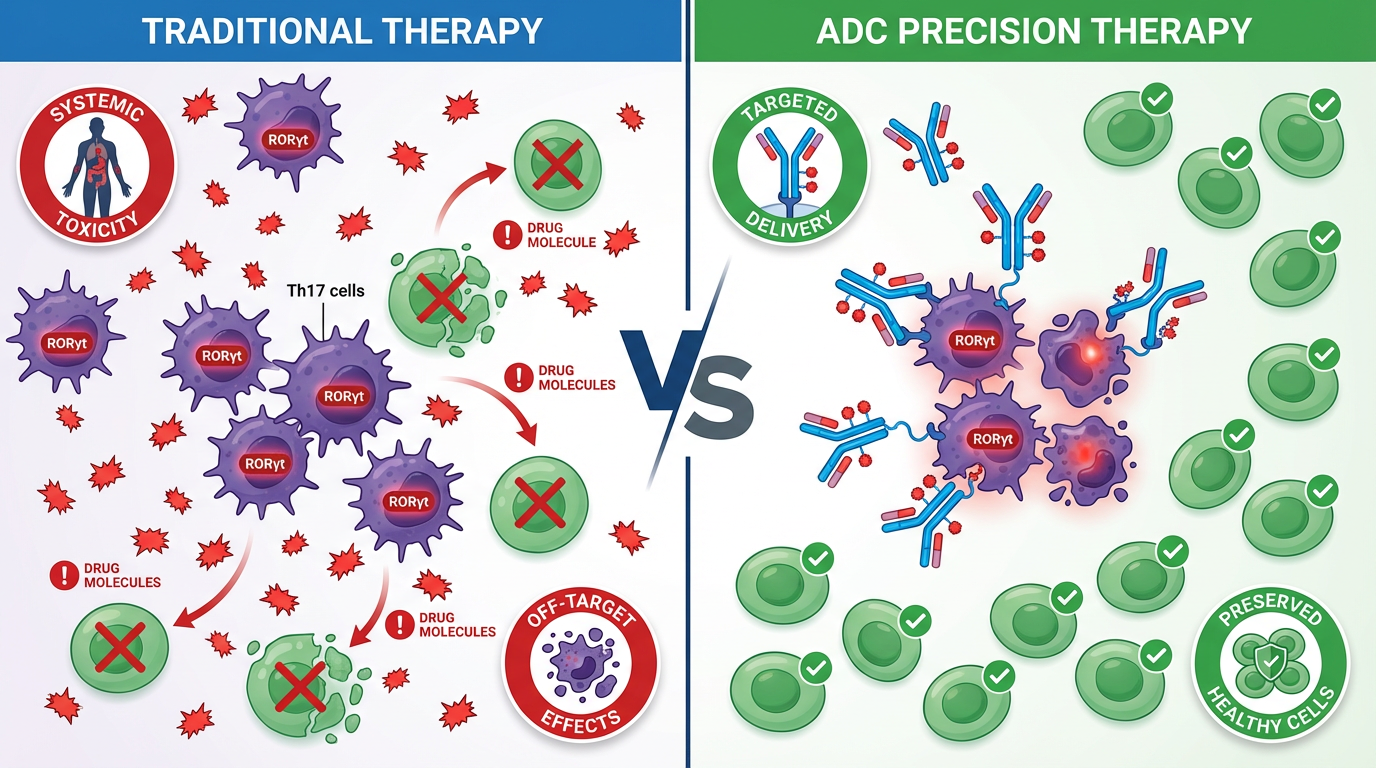
The Problem
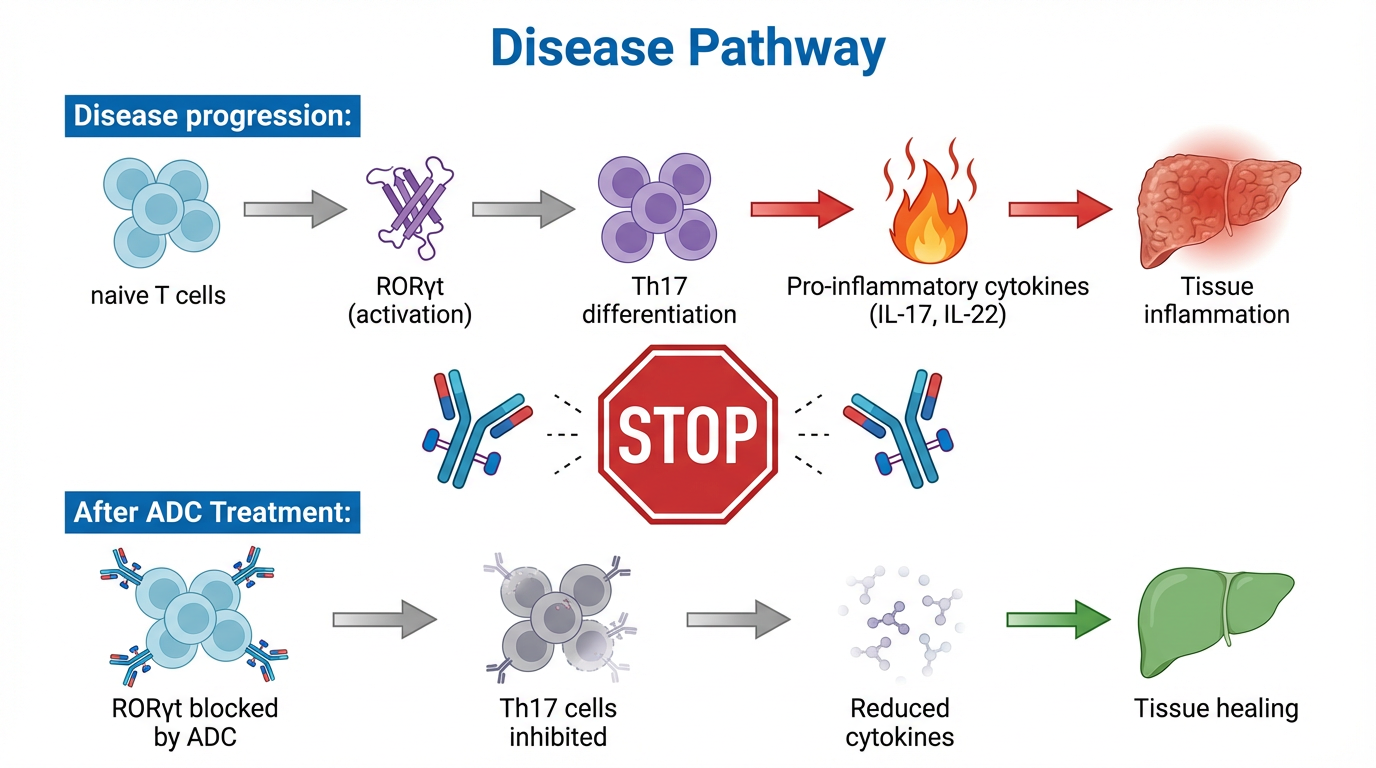
Autoimmune diseases affect millions globally, with current treatments causing severe systemic side effects due to non-specific targeting.
Our Solution
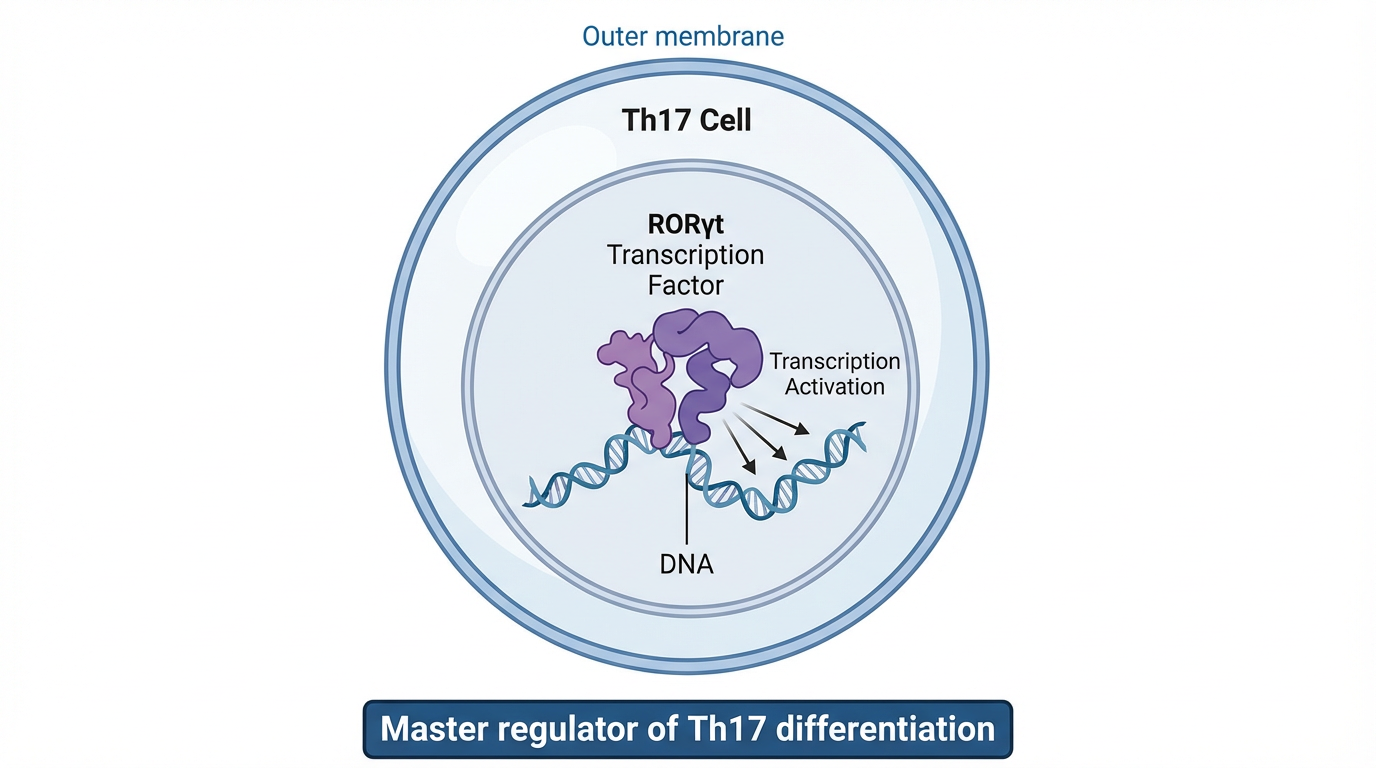
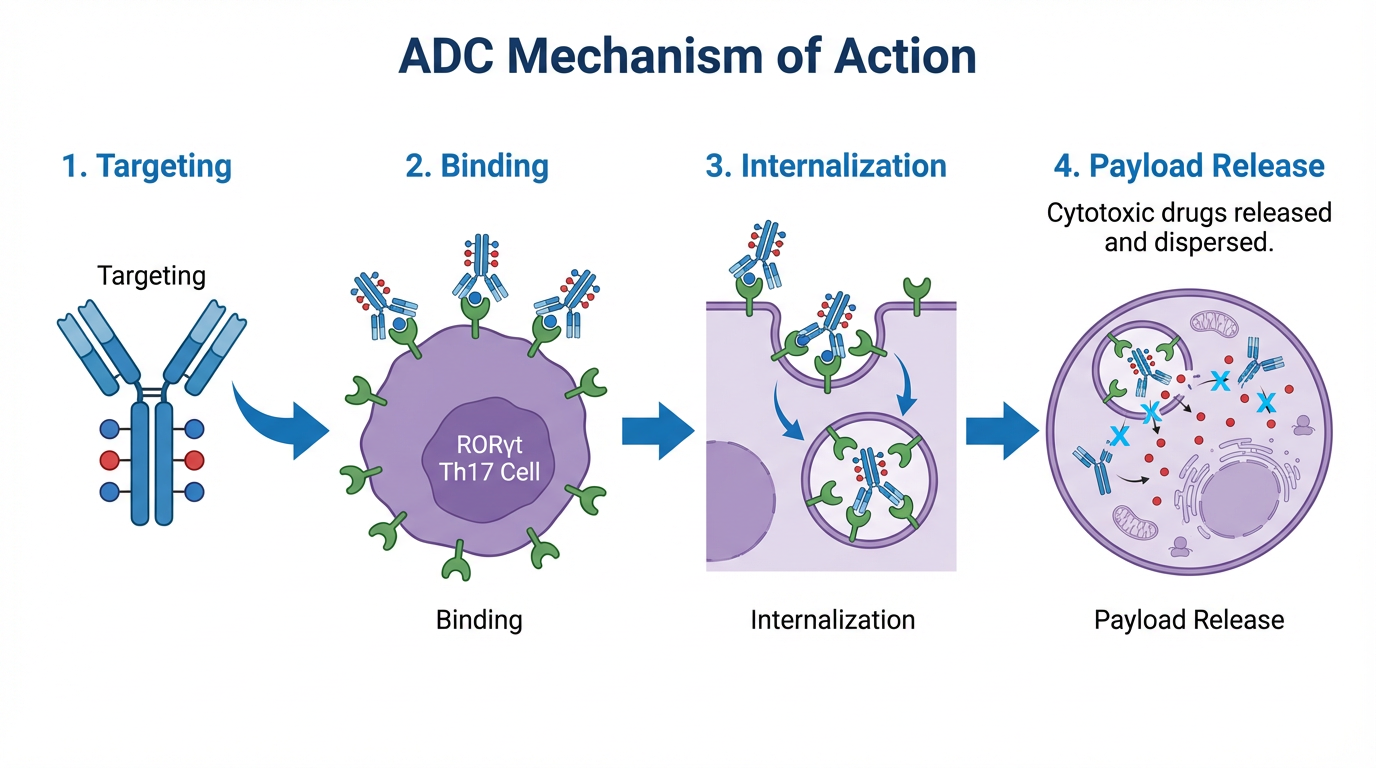
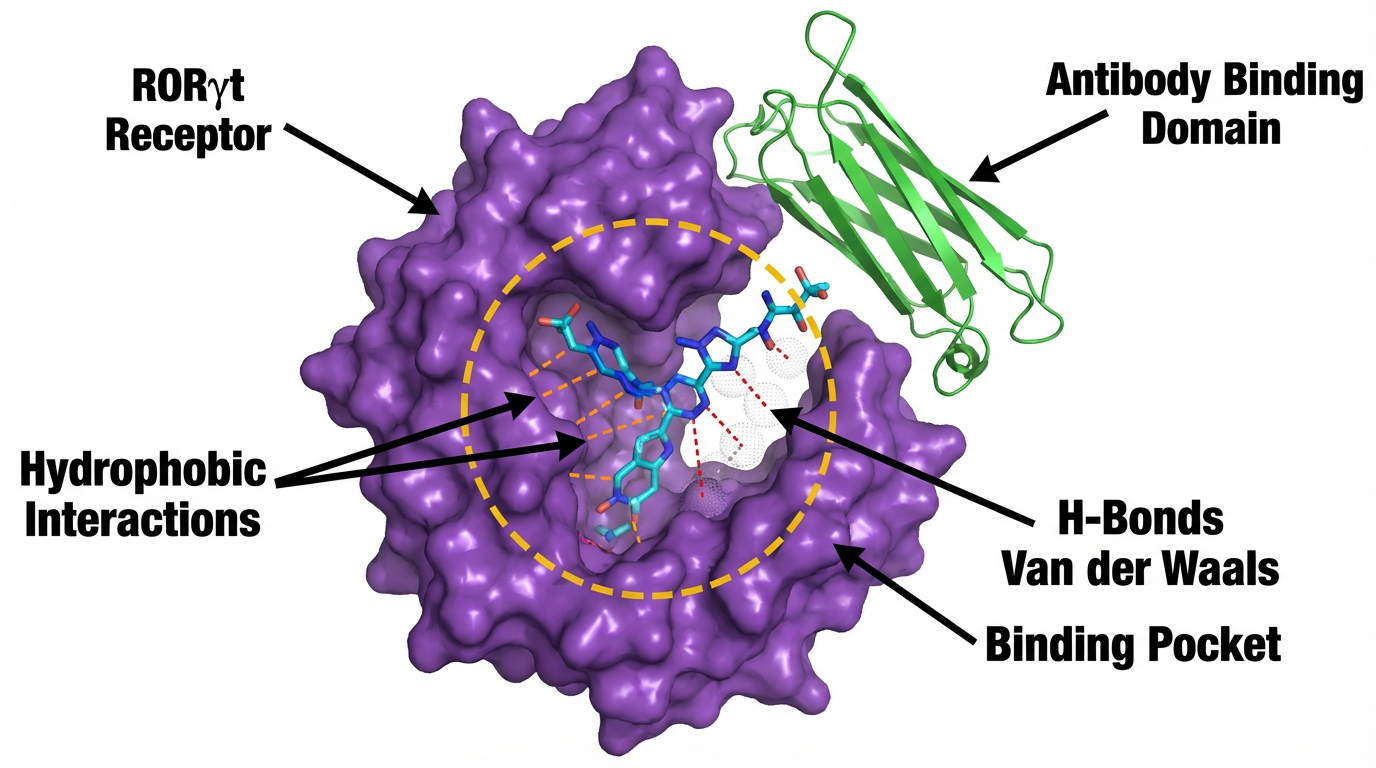
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) targeting RORγt pathway offer precision medicine - delivering therapeutic agents specifically to disease-causing cells while minimizing systemic toxicity.
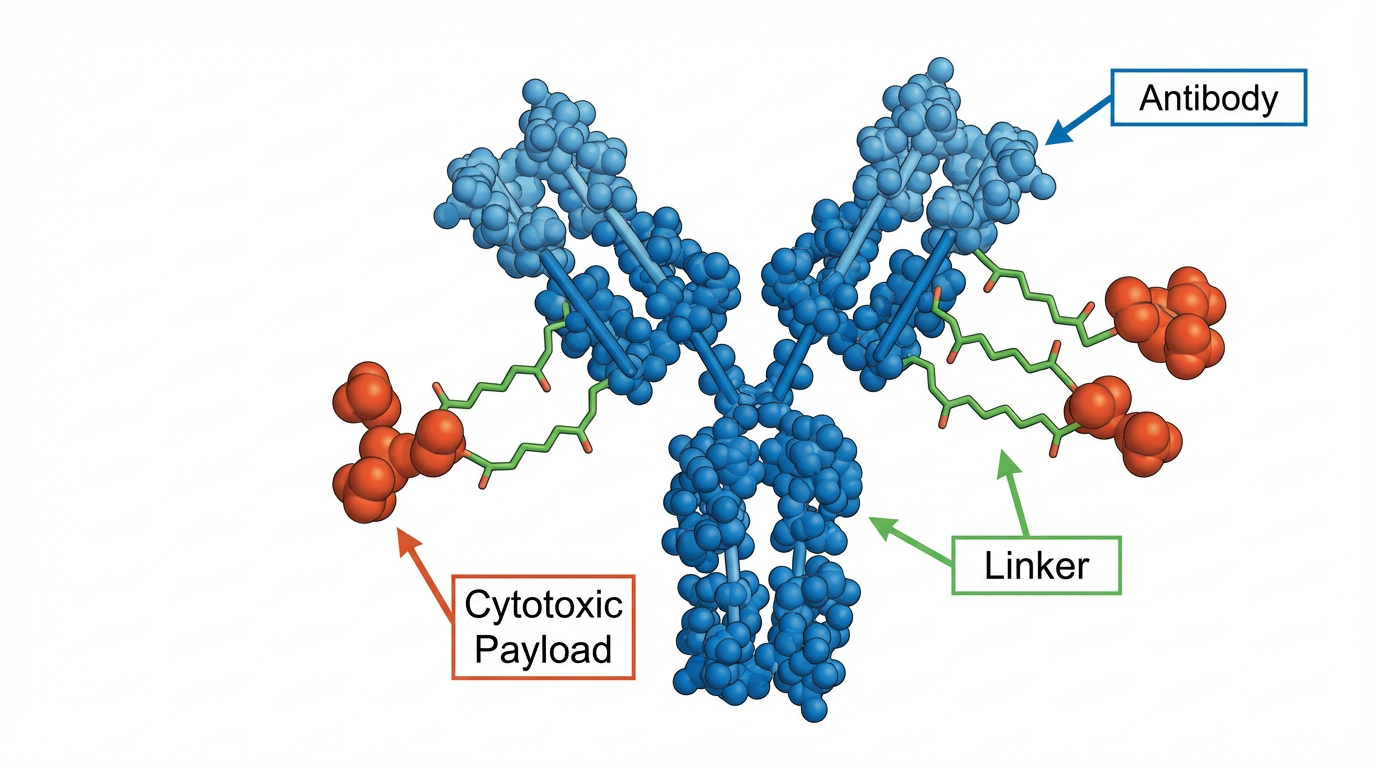
Figure 1: ADC Molecular Structure - Antibody, Linker, and Cytotoxic Payload